Pericardiocentesis
What is Pericardiocentesis?
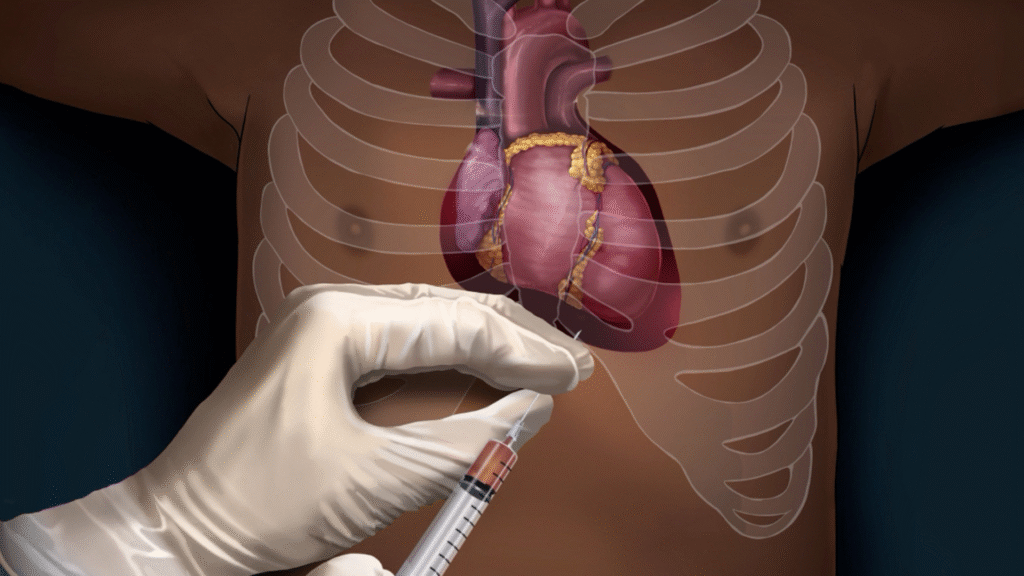
Pericardiocentesis is a life-saving, minimally invasive procedure performed to remove excess fluid from the pericardial sac (the protective membrane surrounding the heart). When this fluid accumulates excessively, it can compress the heart—a condition called cardiac tamponade, which requires urgent intervention.
When is Pericardiocentesis Needed?
Cardiac tamponade (life-threatening)
Large pericardial effusion causing symptoms
Suspected infection (TB pericardial effusion)
Malignant pericardial effusion
Uremic pericarditis
Post-cardiac surgery effusions
Diagnostic sampling of pericardial fluid
Symptoms of Pericardial Effusion
Severe breathlessness
Low blood pressure
Chest discomfort
Rapid heartbeat
Distended neck veins
Procedure Overview: How Pericardiocentesis is Done
Step-by-step:
Patient positioned with head elevated
Local anesthesia given
Needle inserted subxiphoid or apical approach
Guided by echocardiography or fluoroscopy
Fluid aspirated slowly
A pigtail catheter may be left for continuous drainage
Fluid sent for analysis (TB markers, cytology, infection tests)

